글 수 367
출처 : http://danuri.tistory.com/1
http://oss.linbit.com/drbd/
http://www.drdb.org
DRBD(Distributed Replicated Block Device)
DRBD를 쉽게 설명하자면 네트워크 기반의 RAID 1(Mirroring)을 구현해 놓은 것이라고 보면 된다.
네트워크로 물리적으로 떨어진 두대의 서버의 하드디스크 OR 파티션을 미러링 구성을 한것이다.
클러스터링 구성에 LVS 방식은 웹서버일경우 시스템이 죽을경우 다른 시스템이 커버가 가능하겠지만 문제는 항상 일정하게 동기화 되어야 하는 데이타베이스나 파일/이미지 서버가 죽었을경우 이다.
물론 돈을 많이 들여서 스토리지 두개 사서 이중화 솔루션 구매하여 사용할 수 도 있지만 소프트웨어적으로 한번 처리를 해 볼 수 있는 방법을 찾아 볼 수도 있다. 그 해답중의 하나로 DRBD 를 사용 할 수 있다.
DRBD 는 스토리지 이중화라고 생각해도 된다.
이게 파일 베이스로 움직이는게 아니라 블럭 레벨에서 복제가 된다.
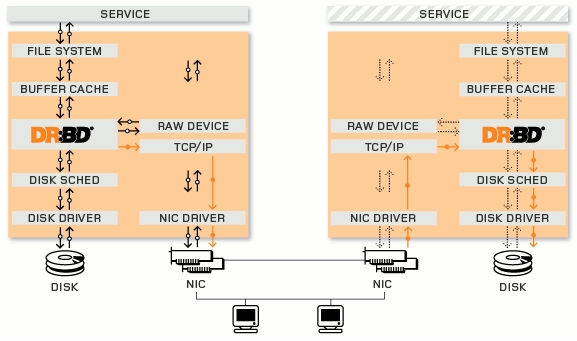
심플한 구성을 생각해 보면,
DRBD를 이용하여 스토리지용으로 하드 용량이 큰 서버 두대를 사용하는데 Heartbeat 를 이용하여 Active/Standby 형태로 구성을 한다. DRBD script 제어를 Heartbeat 에게 맞겨 두고 가상 아이피를 한개 사용하여 외부에서는 가상 아이피로 접근을 한다. 그리고 여기 데이타에 접근을 위해 NFS 를 이용하여 외부에서는 사용을 하게한다. 물론 추후 퍼포먼스등을 고려하여 open-iscsi, gnbd 등 상황에 맞게 사용을 하게 될 것이다. 이렇게 만들어 놓으면 최소한 스토리지 서버가 한대 죽더라도 다른 한대의 서버가 복제된 동일한 내용의 컨텐츠를 가지고 지속적인 서비스가 가능하게 된다. 물론 최소의 비용으로 말이다.
Mysql 의 경우 DRBD를 공식적으로 지원을 하고 있었다.
http://mysql.com/drbd
Mysql Enterprise 용으로 HA 구성시 하나의 방법으로 사용을 하고 있었다.
DRBD 는 linbit 회사에서 공식 기술 지원을 유료로 하고 있다.
http://www.linbit.com/en/products-services/drbd/drbd-support/drbd-support/
노드당 1년에 최소 300만원 이상의 비용이다. 보통 silver 정도 받고 한대로는 운영이 안되므로 두 대의 서버를 사용한다고 하였을때 600*2 하여 1200만원이다. 고 부가가치 기술 지원이다.
http://oss.linbit.com/drbd/
http://www.drdb.org
DRBD(Distributed Replicated Block Device)
DRBD를 쉽게 설명하자면 네트워크 기반의 RAID 1(Mirroring)을 구현해 놓은 것이라고 보면 된다.
네트워크로 물리적으로 떨어진 두대의 서버의 하드디스크 OR 파티션을 미러링 구성을 한것이다.
클러스터링 구성에 LVS 방식은 웹서버일경우 시스템이 죽을경우 다른 시스템이 커버가 가능하겠지만 문제는 항상 일정하게 동기화 되어야 하는 데이타베이스나 파일/이미지 서버가 죽었을경우 이다.
물론 돈을 많이 들여서 스토리지 두개 사서 이중화 솔루션 구매하여 사용할 수 도 있지만 소프트웨어적으로 한번 처리를 해 볼 수 있는 방법을 찾아 볼 수도 있다. 그 해답중의 하나로 DRBD 를 사용 할 수 있다.
DRBD 는 스토리지 이중화라고 생각해도 된다.
이게 파일 베이스로 움직이는게 아니라 블럭 레벨에서 복제가 된다.

심플한 구성을 생각해 보면,
DRBD를 이용하여 스토리지용으로 하드 용량이 큰 서버 두대를 사용하는데 Heartbeat 를 이용하여 Active/Standby 형태로 구성을 한다. DRBD script 제어를 Heartbeat 에게 맞겨 두고 가상 아이피를 한개 사용하여 외부에서는 가상 아이피로 접근을 한다. 그리고 여기 데이타에 접근을 위해 NFS 를 이용하여 외부에서는 사용을 하게한다. 물론 추후 퍼포먼스등을 고려하여 open-iscsi, gnbd 등 상황에 맞게 사용을 하게 될 것이다. 이렇게 만들어 놓으면 최소한 스토리지 서버가 한대 죽더라도 다른 한대의 서버가 복제된 동일한 내용의 컨텐츠를 가지고 지속적인 서비스가 가능하게 된다. 물론 최소의 비용으로 말이다.
Mysql 의 경우 DRBD를 공식적으로 지원을 하고 있었다.
http://mysql.com/drbd
Mysql Enterprise 용으로 HA 구성시 하나의 방법으로 사용을 하고 있었다.
DRBD 는 linbit 회사에서 공식 기술 지원을 유료로 하고 있다.
http://www.linbit.com/en/products-services/drbd/drbd-support/drbd-support/
노드당 1년에 최소 300만원 이상의 비용이다. 보통 silver 정도 받고 한대로는 운영이 안되므로 두 대의 서버를 사용한다고 하였을때 600*2 하여 1200만원이다. 고 부가가치 기술 지원이다.
DRBD
is a block device which is designed to build high availability clusters.
This is done by mirroring a whole block device via (a dedicated) network. You
could see it as a network raid-1.
DRBD takes over the data, writes it to the local disk and sends it to the other
host. On the other host, it takes it to the disk there.
The other components needed are a cluster membership service, which is supposed
to be heartbeat, and some kind of application that works on top of a block
device.
Each device (DRBD provides more than one of these devices) has a state, which
can be 'primary' or 'secondary'. On the node with the primary device the
application is supposed to run and to access the device (/dev/drbdX; used to be
/dev/nbX). Every write is sent to the local 'lower level block device' and to
the node with the device in 'secondary' state. The secondary device simply
writes the data to its lower level block device. Reads are always carried out
locally.
If the primary node fails, heartbeat is switching the secondary device into
primary state and starts the application there. (If you are using it with a
non-journaling FS this involves running fsck)
If the failed node comes up again, it is a new secondary node and has to
synchronise its content to the primary. This, of course, will happen whithout
interruption of service in the background.
And, of course, we only will resynchronize those parts of the device that
actually have been changed. DRBD has always done intelligent resynchronization
when possible. Starting with the DBRD-0.7 series, you can define an "active
set" of a certain size. This makes it possible to have a total resync time of
1--3 min, regardless of device size (currently up to 16TB), even after a hard
crash of an active node.
The ChangeLogs can be found here:
http://git.drbd.org/?p=drbd-8.0.git;a=blob;f=ChangeLog;hb=HEAD
http://git.drbd.org/?p=drbd-8.3.git;a=blob;f=ChangeLog;hb=HEAD
http://git.drbd.org/
The DRBD Homepage is http://www.drbd.org/.
This is done by mirroring a whole block device via (a dedicated) network. You
could see it as a network raid-1.
DRBD takes over the data, writes it to the local disk and sends it to the other
host. On the other host, it takes it to the disk there.
The other components needed are a cluster membership service, which is supposed
to be heartbeat, and some kind of application that works on top of a block
device.
Each device (DRBD provides more than one of these devices) has a state, which
can be 'primary' or 'secondary'. On the node with the primary device the
application is supposed to run and to access the device (/dev/drbdX; used to be
/dev/nbX). Every write is sent to the local 'lower level block device' and to
the node with the device in 'secondary' state. The secondary device simply
writes the data to its lower level block device. Reads are always carried out
locally.
If the primary node fails, heartbeat is switching the secondary device into
primary state and starts the application there. (If you are using it with a
non-journaling FS this involves running fsck)
If the failed node comes up again, it is a new secondary node and has to
synchronise its content to the primary. This, of course, will happen whithout
interruption of service in the background.
And, of course, we only will resynchronize those parts of the device that
actually have been changed. DRBD has always done intelligent resynchronization
when possible. Starting with the DBRD-0.7 series, you can define an "active
set" of a certain size. This makes it possible to have a total resync time of
1--3 min, regardless of device size (currently up to 16TB), even after a hard
crash of an active node.
The ChangeLogs can be found here:
http://git.drbd.org/?p=drbd-8.0.git;a=blob;f=ChangeLog;hb=HEAD
http://git.drbd.org/?p=drbd-8.3.git;a=blob;f=ChangeLog;hb=HEAD
http://git.drbd.org/
The DRBD Homepage is http://www.drbd.org/.

